Electrophysiology (EP) Study
An Electrophysiology (EP) Study is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart and identify abnormal heart rhythms, also known as arrhythmias. This test helps pinpoint the source of arrhythmias, allowing doctors to determine the best course of treatment, such as medication, ablation, or the implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator.
Procedure
- Preparation: The patient is mildly sedated, and a local anesthetic is applied at the catheter insertion site, typically in the groin, arm, or neck.
- Catheter Insertion: Thin, flexible wires called electrode catheters are inserted into a vein and guided into the heart using real-time X-ray imaging.
- Mapping Electrical Activity: The electrodes detect the heart’s electrical signals and create a detailed map of its electrical pathways. This allows the physician to identify any irregular heartbeats or abnormal electrical circuits.
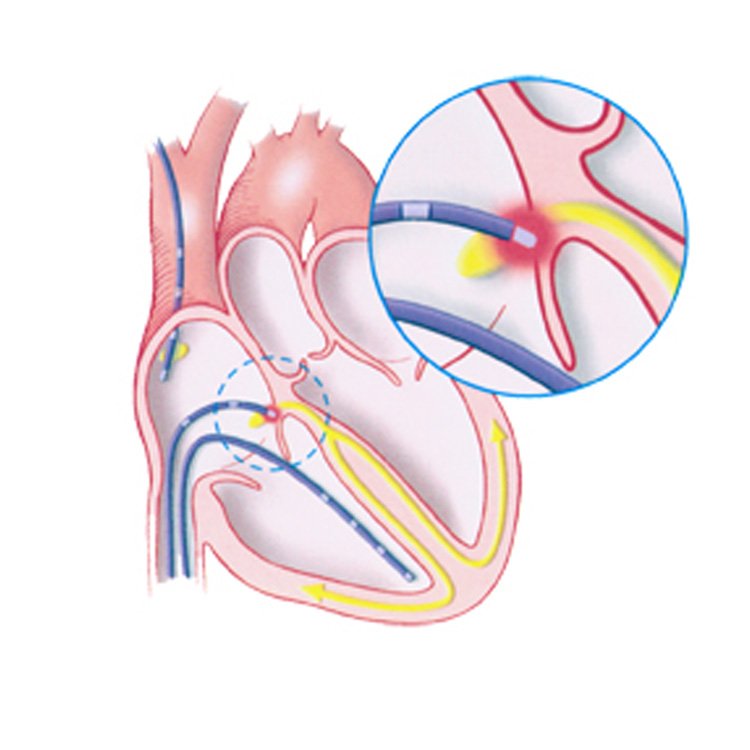
- Arrhythmia Induction: The doctor may stimulate the heart to provoke an abnormal rhythm under controlled conditions to study how and where the arrhythmia starts.
- Ablation (Optional): If the source of the arrhythmia is identified, the doctor may perform radiofrequency ablation, where the abnormal tissue is destroyed to correct the rhythm problem.
Benefits
- Diagnosis of complex arrhythmias.
- Guides treatment: Helps in deciding the need for a pacemaker, medication, or ablation.
- Minimally invasive: No need for major surgery.
Risks
Potential risks include bleeding, infection, or rare complications like heart damage or stroke, but these are uncommon.
Youtube link- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_WkTQB4ARfM
